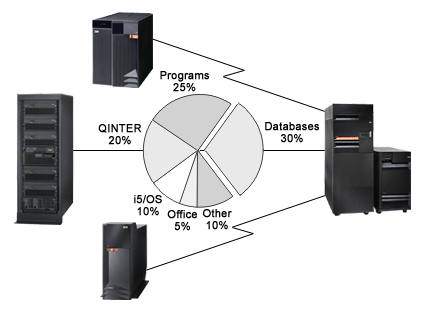
An OptiConnect cluster will usually have a database system and one or more application systems. The system where the database resides is the database system, and the systems that contain the applications are called application systems. The OptiConnect software allows a program on the application system to make database changes or database queries on the database system. Central Processing Unit (CPU) work load ratios of under 30% database and 70% application will benefit the most by distributing work loads between systems in the OptiConnect network. Figure 6 illustrates an example of this type of setup.

Another important consideration is whether the application is batch or interactive. This clustering technology is optimal for interactive workloads. Batch workloads require special considerations and may not be appropriate for use in an OptiConnect environment. However, solutions can be designed to effectively handle a mixture of batch and interactive workloads, as well as multiple database and application methods. Applications with heavy database activity and large numbers of file open and close operations may not realize the full potential of the OptiConnect technology.
When a program opens a database file, the associated DDM file or RDB entry identifies the database system name. The OptiConnect Connection Manager on the application system sends the database request to the database system by using a fast device driver. The OptiConnect communication link provides access at a fraction of the DDM system overhead because its communications protocol operates only in a specific shared bus environment. The OptiConnect Connection Manager connects the request with an agent job on the database system. Agent jobs work with the database code to issue the request and route the result back to the application system.