 Figure 8. Advanced configuration
Figure 8. Advanced configuration
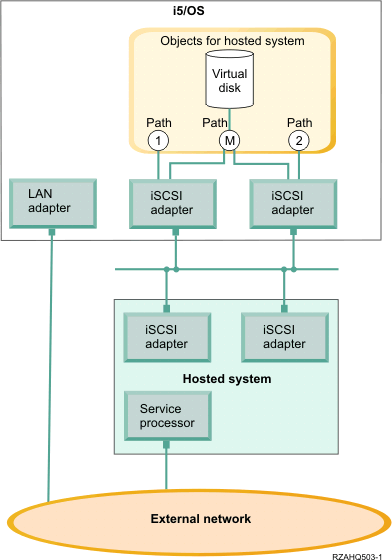



A single iSCSI HBA for iSeries™ is capable of supporting several servers or hosted systems. Each hosted system is also capable of connecting to multiple iSCSI HBAs for iSeries. Figure 8 illustrates a hosted system that is connected to more than one iSCSI HBA for iSeries.
 Figure 8. Advanced configuration
Figure 8. Advanced configuration


Figure 8 shows multiple iSCSI HBAs installed in the hosted system.
Path definition
When a hosted system
is connected to an iSCSI HBA for iSeries a path is defined between the hosted
system and the iSCSI HBA for iSeries.
There are several distinct paths defined in Figure 8. These are labelled 1, 2 and M.
A virtual device being hosted in an iSeries server is said to be found behind a path. A configured virtual disk (for example Drive C:) hosted in i5/OS™ by an iSCSI HBA for iSeries or NWSH adapter is found behind that NWSH adapter.
In Figure 8, paths 1 and 2 are each defined for a separate iSCSI HBA for iSeries. Devices defined in path 1 can only be found behind the iSCSI adapter where the path is defined. Similarly, devices defined in path 2 can only be found behind the iSCSI adapter where the path is defined. Any devices defined behind path 1 or 2 are said to be found exclusively behind their specific iSCSI HBA.
Introduction to multi-path
A hosted system
can have redundant paths to access virtual disks hosted by i5/OS. The most comprehensive
case is when there are redundant paths at each end. A given virtual disk can
be accessed from the hosted system using either of the two iSCSI HBAs installed
in the hosted system and found in the iSeries using either one of the two iSCSI HBAs
for iSeries. This is known as multi-path.
In Figure 8 the multi-path is defined as M. Virtual disks found behind the multi-path can be accessed by either one of the iSCSI HBAs that are installed in the iSeries server. A multi-path is defined as a group of iSCSI HBAs for iSeries that can access or use path M. Only one multi-path group can be defined per hosted system. This group can include more than one iSCSI HBA for iSeries.
Dedicated Bandwidth
There are cases where
redundant paths may not be wanted or required, but virtual disks requiring
higher performance may need a dedicated path.
In Figure 8, a hosted system configuration can define a virtual disks behind path 1 or 2 instead behind of behind path M. This way, an iSCSI adapter's bandwidth can be dedicated to certain virtual disks.

