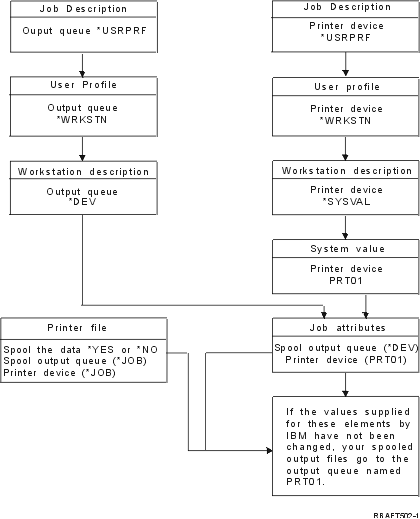
Routing process order
Assuming that the method used to start the job does not override the output
queue or printer device values, the following order is followed:
- The job initiation phase begins. The system looks at the following:
- The output queue value in the job description.
- The output queue value in the user profile.
- The output queue value in the workstation description.
- The printer device value in the job description.
- The printer device value in the user profile.
- The printer device value in the workstation description.
- The system value Default printer (QPRTDEV). If the printer identified
in the system value does not exist, the output goes to the QPRINT output queue.
The results of this phase determine the job attributes.
- The job run time phase begins. The system looks at the following:
- The output queue value in the printer file.
- The output queue value in the job attributes.
- The printer device value in the printer file.
- The printer device value in the job attributes.
- The SPOOL value in the printer file.
The results of this phase determine the output queue name or printer
device name to where the spooled file is routed.
The following figure shows the printing elements and how they relate to
the printing process.
The CHGJOB CL command allows you to override the
output queue and printer device values. The OVRPRTF CL
command allows you to override many printer file values including the output
queue and printer device values. See Printer file overrides for more
information on overriding printer file values.
Printing in a batch environment
When a user signs on to the server, an output queue (OUTQ) and a printer
device (PRTDEV) are established for that job.
The names for the output queue and printer device are resolved when the
system searches through the user profile, job description, workstation description,
and system values.
A similar process occurs when batch jobs are started on the system, with
two differences:
- The output queue and printer device values are passed to the batch job
from the job that started it. This means that no resolution of the output
queue and printer device needs to be done.
- The value *WRKSTN has no real meaning because batch jobs do not have an
associated workstation. If *WRKSTN is encountered in the resolution of output
queue and printer device, *WRKSTN is replaced with *DEV if output queue is
being resolved and *SYSVAL if printer device is being resolved.

