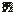Unprintable double-byte characters
A double-byte character is considered unprintable if its double-byte code
is not in the valid range or if its double-byte code is valid but does not
have a character image defined.
You can specify that the system replace unprintable double-byte characters
by specifying the replace unprintable character parameter (RPLUNPRT(*YES))
on the CRTPRTF, CHGPRTF, or OVRPRTF command, but you cannot choose the replacement
character.
Although you cannot choose the replacement character for unprintable double-byte
characters, you can choose the replacement character for unprintable alphanumeric
characters. To improve system performance, select a blank ( ) as the
replacement character for unprintable alphanumeric characters.
When the system finds an unprintable double-byte character during printing,
the following happens:
- If you specify RPLUNPRT(*YES), the system does not send a message when
it finds unprintable characters. Instead, the system prints unprintable extended
characters as either the double-byte underline (__) when you specify
extended character processing, or as an undefined character when you do not
specify extended character processing.
For Japanese printers, the default
symbol used is:
For Chinese and Korean printers, the default symbol used is the
underscore.
The system prints unprintable basic double-byte characters
as double-byte blanks.
- If you specify RPLUNPRT(*NO), the system sends an inquiry message when
it finds unprintable characters. You have the following options:
- Hold the spooled file.
- Continue printing where the unprintable character was encountered. If
you continue printing, the system sends the inquiry message that you just
received. It is sent each time the system finds an unprintable character,
regardless of your response to the first message.
- Continue printing by specifying a page number where printing should continue.
When the system finds subsequent unprintable characters, it processes the
characters as if the file were specified with RPLUNPRT(*YES). See the item
in this list about RPLUNPRT(*YES) for a description of how the system processes
these characters.
If the system finds invalid double-byte code, it stops processing double-byte
extended characters and prints them as the undefined character.