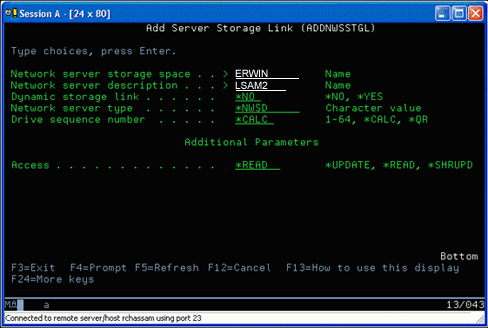
Use the Add Network Server Storage Link command
To link a disk drive using the Add Network Server Storage Link command,
follow these instructions:
The following is an example of the using the mount command to mount
a file system as read-only:
mount -o ro /dev/hdb1 /mnt/data2
An entry in the /etc/fstab file to mount a disk resource as read-only would resemble the following:
/dev/hdb1 /mnt/data ext2 ro 1 1
Update and provide users access
To update a shared storage space and provide users access, follow
these steps:
- Give all users *SHRUPD access to the storage space.
- Have all users open the storage space concurrently for read-only access.
- Have all users stop accessing the data on that storage space and close (unmount) that device from within Linux.
- Have one user open the device for read-write access, update the data, and close the device.
- Have all users reopen the device for read-only concurrent access.
Other restrictions:
- Version 5 Release 2 or later of i5/OS® is required, but it does not have to be in the primary partition.
- The maximum size supported for a storage space is 1000 GB.
- The maximum number of storage spaces supported is 64. However, while 64 storage spaces may be linked to the server, only the first 20 storage spaces are visible to Linux, depending on the Linux distribution.