To use quality of service (QoS) policies, network equipment (like routers and switches) must have the capability for traffic conditioners. Traffic conditioners refer to classifiers, meters, markers, shapers, and droppers.
If the network equipment has all the traffic conditioners, then it is considered DiffServ-aware.
Note: These hardware requirements are not iSeries™ specific. You will not see these
terms used in the QoS interface, because the server cannot control external
hardware. Outside a private network, hardware needs to have the ability to
handle general QoS requirements. Check with the specific equipment manuals
to make sure that they can handle differentiated service requirements. It
is also recommended that you research general QoS concepts and prerequisites
before implementing policies.
The following figure shows a logical representation of how traffic conditioners work.
Figure 1. Traffic conditioners
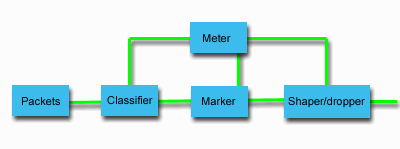

The following information describes each of the traffic conditioners in more detail.
- Classifiers
- Packet classifiers select packets in a traffic stream, based on the content in its IP header. The iSeries server defines two types of classifiers. The behavior aggregate (BA) classifies packets, based exclusively on the differentiated services codepoint. The multi-field (MF) classifier selects packets, based on the value of a combination of one or more header fields, such as source address, destination address, differentiated services field, protocol ID, source port, Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), server type and destination port numbers.
- Meters
- Traffic meters measure whether the IP packets, being forwarded by the classifier, are corresponding to the traffic's IP header profile. The information in the IP header is determined by the values you set in the QoS policy for this traffic. A meter passes information to other conditioning functions to trigger an action. The action is triggered for each packet whether it is in-profile or out-of-profile.
- Markers
- Packet markers set the differentiated services (DS) field. The marker can be configured to mark all packets to a single codepoint or to a set of codepoints used to select a per-hop behavior.
- Shapers
- Shapers delay some or all of the packets in a traffic stream to bring the stream into compliance with the traffic profile. A shaper has a finite buffer size, and routers might discard packets if there is not enough space to hold the delayed packets.
- Droppers
- Droppers discard some or all of the packets in a traffic stream. This occurs to bring the stream into compliance with the traffic profile.