For each PDML project file, the GUI Builder generates a help skeleton and puts it into a single HTML document. Before use, this HTML file is broken up into single topic HTML files for each dialog of the PDML project. This provides the user with granular help for each topic and allows you to manage only a few large help files.
The Help Document is a valid HTML file and can be viewed in any browser and edited using most HTML editors. Tags that define the sections in a Help Document are embedded within comments, so they do not show up in a browser. The comment tags are used to break the Help Document into several sections:
- Header
- Topic section for each dialog
- Topic section for each control that is help-enabled
- Footer
In addition, you can add additional topic sections before the footer to provide additional information or common information. Topic sections have only the html body until they are split, when a header and footer are created. When the Help Document is split up, the processor adds a header and footer to the topic section to make a complete HTML file. The header and footer from the Help Document are used as default header and footer. However, you can override the default header with your own.
Inside the Help Document
The following sections explain the parts of the Help Document:
- Header
- The end of the header section is shown by the following tag:
<!-- HELPDOC:HEADEREND -->
If you want to override the default header for all of the individual topics when they are split, use the HEADER keyword and provide the name of an html fragment to include. For example:<!-- HELPDOC:HEADEREND HEADER="defaultheader.html" -->
- Topic segment
- Each topic is surrounded by the following tags:
<!-- HELPDOC:SEGMENTBEGIN -->
and<!-- HELPDOC:SEGMENTEND -->
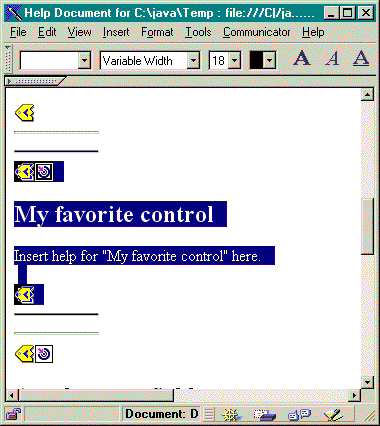
Immediately following the SEGMENTBEGIN tag is an anchor tag which names the segment. It also provides the file name of the HTML document that is created when the Help Document is split. The name of the segment combines the panel identifier, control identifier, and future file extension (html). For example: "MY_PANEL.MY_CONTROL.html" Segments for panels have only the panel identifier and future file extension.The help generator will place text in the document indicating where you place your help information:
<!-- HELPDOC:SEGMENTBEGIN PDMLSYNCH="YES" --><A NAME="MY_PANEL.MY_CONTROL.html"></A> <H2>My favorite control</H2> Insert help for "My favorite control" here. <P><!-- HELPDOC:SEGMENTEND -->
You can add additional HTML 2.0 tags as needed after the anchor tag and before the SEGMENTEND tag.
The PDMLSYNCH tag controls how closely a segment is tied to the controls defined in PDML. If PDMLSYCH is "YES", the Help Document segment will be removed if the control of the same name is removed in the PDML. PDMLSYNCH="NO" indicates the topic must be kept in the Help Document regardless of whether a corresponding control exists in the PDML. This is used, for example, when you create additional topics for depth or a common topic.
The help generated for a panel has links to each control enabled for help on the panel. These links are generated with a local anchor reference, so that you can test them as internal links in a standard browser. When the Help Document is split, the processor removes the "#" on these internal links making them external links in the resulting single topic HTML files. Because you may want to have internal links within a topic, the processor only removes any preceding "#" when the reference has ".html" embedded in it.
If you want to override the default header for any particular topic, use the HEADER keyword and provide the name of an html fragment to include. For example:
<!-- HELPDOC:SEGMENTBEGIN PDMLSYNCH="YES" HEADER="specialheader.html" -->
- Footer
- The footer in the Help Document begins with the following tag:
<!-- HELPDOC:FOOTERBEGIN -->
The standard footer is </BODY></HTML>This footer is added to each HTML file.
Adding links
You can add links to any external or internal URL as well as any other segment. However, you must follow some conventions:
- External URLs are used in the standard manner. This includes internal links to external URLs
- Internal links within the same topic are written in the standard way, but must not have ".html" as part of the tag name. This is because the Help Document processor assumes that any link with .html will need to be an external link when the topics are separate. Therefore, it removes the preceding "#".
- Links to other topic segments must be written with a preceding "#" as though they are an internal anchor reference.
- Internal links to other topic segments may also be created. Only the leading "#" is removed during processing.
- At run-time, the PanelManager class looks for help files in a subdirectory with the same name as the PDML file. When the processor splits the Help Document, it creates this subdirectory by default and places the resulting HTML files in it.
- The processor does not make any adjustments for external URL references that are relative links. When you link from an individual topic file, any relative links will be searching from the new subdirectory. Therefore, you will need to place copies of resources such as images where they can be found or use "../" in the path in order to search from the panel directory.
Editing using a visual editor
You can edit your help content in almost any visual HTML editor. Because the HELPDOC tags are comments they may not be obvious in some editors. For convenience, a horizontal rule is added to the help skeleton immediately before the SEGMENTBEGIN tag and immediately after the SEGMENTEND tag. These horizontal rules provide clear visual indication of the entire segment in a visual editor. If you select a segment because you want to move, copy, or delete it, select the surrounding horizontal rules to be sure you have included the SEGMENTBEGIN and SEGMENTEND tags in your selection. These horizontal rules are not copied to the final individual HTML files.
Creating Additional Topics
You can create additional topic segments in the Help Document. It is often easiest to do this by copying another segment. When you copy the segment, you must copy the horizontal rules just before the SEGMENTBEGIN and after the SEGMENTEND tag. This will make future visual editing much easier and help avoid mismatched tags. For best results, use the following tips:
- The name of the anchor must be the name you want for the resulting single file when the Help Document is split. It must end in ".html".
- Use the PDMLSYNCH="NO" keyword on the SEGMENTBEGIN tag to prevent the segment from being removed if the help skeleton is regenerated.
- Any references to your new topic will be made as an internal link in the Help Document with a preceding "#". This "#" will be removed in later processing when the segments are split into single files.
Checking Your Links
For most writing, you can check your links by viewing your document in a Web browser and selecting different links. In the single Help Document, the links are still in their internal form.
As you reach completion, or when you want to test with the application you are developing help for, you will need to break the Help Document into single files. You do this with Help Document to HTML Processing.
If you need to regenerate the Help Document after editing, your writing will be preserved. You may want to regenerate the Help Document if you add new controls after generating the original help skeleton. In this case, the help generator checks for an existing Help Document before it creates a new skeleton. If one is found, it preserves any existing segments and then adds the new controls.