Use this example to create a single server job that handles all incoming connections. When the accept() API is completed, the server handles the entire transaction.
The figure illustrates how the server and client jobs interact when the system used the iterative server design.
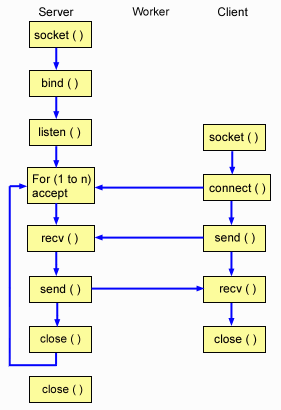
Flow of socket events: Iterative server
The following sequence of the socket calls provide a description of the graphic. It also describes the relationship between the server and worker applications. Each set of flows contain links to usage notes on specific APIs. If you need more details on the use of a particular API, you can use these links. The following sequence shows the function calls for the iterative server application:
- The socket() function returns a socket descriptor representing an endpoint. The statement also identifies that the INET (Internet Protocol) address family with the TCP transport (SOCK_STREAM) is used for this socket.
- After the socket descriptor is created, the bind() function gets a unique name for the socket.
- The listen() allows the server to accept incoming client connections.
- The server uses the accept() function to accept an incoming connection request. The accept() call blocks indefinitely waiting for the incoming connection to arrive.
- The recv() function receives data from the client application.
- The send() function echoes the data back to the client.
- The close() function closes any open socket descriptors.
Note: By using the code examples, you agree to the terms of the Code license and disclaimer information.
/**************************************************************************/
/* Application creates an iterative server design */
/**************************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#define SERVER_PORT 12345
main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i, len, num, rc, on = 1;
int listen_sd, accept_sd;
char buffer[80];
struct sockaddr_in addr;
/*************************************************/
/* If an argument was specified, use it to */
/* control the number of incoming connections */
/*************************************************/
if (argc >= 2)
num = atoi(argv[1]);
else
num = 1;
/*************************************************/
/* Create an AF_INET stream socket to receive */
/* incoming connections on */
/*************************************************/
listen_sd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listen_sd < 0)
{
perror("socket() failed");
exit(-1);
}
/*************************************************/
/* Allow socket descriptor to be reuseable */
/*************************************************/
rc = setsockopt(listen_sd,
SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR,
(char *)&on, sizeof(on));
if (rc < 0)
{
perror("setsockopt() failed");
close(listen_sd);
exit(-1);
}
/*************************************************/
/* Bind the socket */
/*************************************************/
memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr));
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
addr.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT);
rc = bind(listen_sd,
(struct sockaddr *)&addr, sizeof(addr));
if (rc < 0)
{
perror("bind() failed");
close(listen_sd);
exit(-1);
}
/*************************************************/
/* Set the listen back log */
/*************************************************/
rc = listen(listen_sd, 5);
if (rc < 0)
{
perror("listen() failed");
close(listen_sd);
exit(-1);
}
/*************************************************/
/* Inform the user that the server is ready */
/*************************************************/
printf("The server is ready\n");
/*************************************************/
/* Go through the loop once for each connection */
/*************************************************/
for (i=0; i < num; i++)
{
/**********************************************/
/* Wait for an incoming connection */
/**********************************************/
printf("Interation: %d\n", i+1);
printf(" waiting on accept()\n");
accept_sd = accept(listen_sd, NULL, NULL);
if (accept_sd < 0)
{
perror("accept() failed");
close(listen_sd);
exit(-1);
}
printf(" accept completed successfully\n");
/**********************************************/
/* Receive a message from the client */
/**********************************************/
printf(" wait for client to send us a message\n");
rc = recv(accept_sd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0);
if (rc <= 0)
{
perror("recv() failed");
close(listen_sd);
close(accept_sd);
exit(-1);
}
printf(" <%s>\n", buffer);
/**********************************************/
/* Echo the data back to the client */
/**********************************************/
printf(" echo it back\n");
len = rc;
rc = send(accept_sd, buffer, len, 0);
if (rc <= 0)
{
perror("send() failed");
close(listen_sd);
close(accept_sd);
exit(-1);
}
/**********************************************/
/* Close down the incoming connection */
/**********************************************/
close(accept_sd);
}
/*************************************************/
/* Close down the listen socket */
/*************************************************/
close(listen_sd);
}