- From a multithreaded process and path refers to a shell script that does not exist in a threadsafe file system.
/QSYS.LIB/MYLIB.LIB/MYPROG.PGM
See QlgSpawn()--Spawn Process (using NLS-enabled path name) for an example specifying the program using the Qlg_Path_Name_T structure. The Qlg_Path_Name_T structure is supported by QlgSpawn() and allows the program name to be specified in any CCSID.
Note: For more information about path syntaxes for the different file systems, see the Integrated file system information in the Files and file systems topic.
- Library list
- Language identifier
- Country or region identifier
- Coded character set identifier
- Default coded character set identifier
- Locale (as specified in the user profile)
The child process has the same user profile as the calling thread. However, the i5/OS job attributes come from the job description specified for the prestart job entry, and the run attributes come from the class that is associated with the i5/OS subsystem used for the prestart job entry.
Notes:
- The prestart job entry QP0ZSPWP is used with prestart jobs that will not be
creating threads. The prestart job entry QP0ZSPWT is used with prestart jobs
that will allow multiple threads. Both types of prestart jobs may be used in
the same subsystem. The prestart job entry must be defined for the subsystem
that the spawn() parent process runs under in order for it to
be used.
- The following example defines a prestart job entry (QP0ZSPWP) for use by
spawn() under the subsystem QINTER. The
spawn() API must have the SPAWN_SETPJ_NP flag set (but not
SPAWN_SETTHREAD_NP) in order to use these prestart jobs:
ADDPJE SBSD(QSYS/QINTER) PGM(QSYS/QP0ZSPWP) INLJOBS(20) THRESHOLD(5) ADLJOBS(5) JOBD(QGPL/QDFTJOBD) MAXUSE(1) CLS(QGPL/QINTER) - The following example defines a prestart job entry (QP0ZSPWT) that will
create prestart jobs that are multithread capable for use by
spawn() under the subsystem QINTER. The spawn() API
must have both SPAWN_SETPJ_NP and SPAWN_SETTHREAD_NP flags set in order to use
these prestart jobs. Also, the JOBD parameter must be a job description that
allows multiple threads as follows:
ADDPJE SBSD(QSYS/QINTER) PGM(QSYS/QP0ZSPWT) INLJOBS(20) THRESHOLD(5) ADLJOBS(5) JOBD(QSYS/QAMTJOBD) MAXUSE(1) CLS(QGPL/QINTER)
Refer to the Work Management topic for complete details on prestart jobs.
#!interpreter_path <options>
where interpreter_path is the path to the shell interpreter program.
If the calling process is multithreaded, path (the first parameter to spawn()) must reference a threadsafe file system.
spawn() calls the shell interpreter, passing in the shell options and the arguments passed in as a parameter to spawn(). The argument list passed into the shell interpreter will look like Arguments to Shell Interpreter.
Arguments to Shell Interpreter
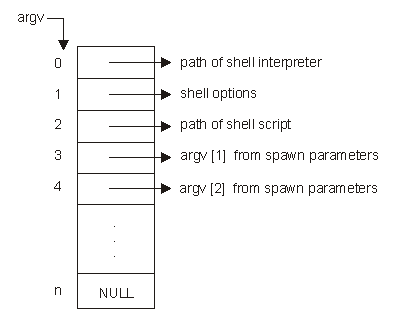
See About Shell Scripts for an example using spawn() and shell scripts.
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
}
where the following are true:
- argc is the number of arguments in argv[].
- argv[] is an array of arguments represented as null-terminated character strings.
- The last entry in the array is NULL.
- The first element in the array, argv[0], is automatically set to the name of the program. Any value specified for argv[0] during the call to spawn() will be overwritten.
- The remaining argv[] elements, if any, will correspond directly to the argv[] elements specified during the call to spawn().
The maximum number of arguments that can be specified is dependent on the following:
- The maximum number of parameters allowed for the program that is run in the child process, as seen by the DSPPGM CL command. Some programs allow up to 65 535 parameters, while others may only allow up to 255 parameters. The value of SPAWN_MAX_NUM_ARGS is 255, in order to maintain compatibility with programs that only allow up to 255 parameters. If the maximum number is exceeded, spawn() returns -1 with errno set to E2BIG.
- The total size required for containing the arguments, which includes the array of pointers to strings, and the total size of all the strings. The total size is limited to approximately 16 500 000 bytes. If the total size is exceeded, spawn() returns -1 with errno set to ENOMEM.
Note: If the user of spawn() specifies the extern variable environ as the envp[] parameter, the user must successfully call one of the following APIs before calling spawn():
- getenv()
- putenv()
- Qp0zGetEnv()
- Qp0zInitEnv()
- Qp0zPutEnv()
The extern variable environ is not initialized until one of these APIs is called in the current activation group. If environ is used in a call to spawn() without first calling one of these APIs, spawn() returns an error.
- File descriptor 0, 1, and 2 are allocated to the first three files that
have descriptors allocated to them. If an application writes to file descriptor
1 assuming it is stdout, the result will not be as expected.
- Any API that assumes stdin, stdout, and stderr are file descriptors 0, 1, and 2 will not behave as expected.
Users and applications can enable descriptor-based standard I/O for child processes by setting environment variable QIBM_USE_DESCRIPTOR_STDIO to the value Y in the child process. This can be accomplished on the call to spawn() by either of the following:
- Specifying the extern variable environ as the
envp[] parameter. This assumes that the QIBM_USE_DESCRIPTOR_STDIO
environment variable exists in the calling process.
The environment variable can be set by using one of the following:
- API putenv("QIBM_USE_DESCRIPTOR_STDIO=Y");
- Command ADDENVVAR ENVVAR(QIBM_USE_DESCRIPTOR_STDIO) VALUE(Y)
- Command CHGENVVAR ENVVAR(QIBM_USE_DESCRIPTOR_STDIO) VALUE(Y)
- Explicitly include "QIBM_USE_DESCRIPTOR_STDIO=Y" in the user-defined envp[] array with the "name=value" strings.
If you enable descriptor-based standard I/O for child processes, file
descriptors 0, 1, and 2 are automatically used for stdin, stdout, and stderr,
respectively. However, spawn() must be called using a
fd_map that has file descriptors 0, 1, and 2 properly allocated. See About Shell Scripts for an example that enables
descriptor-based standard I/O for a child process. Refer to the WebSphere Development Studio: ILE
C/C++ Programmer's Guide for
complete details on this support.
for
complete details on this support.
To help the user start a debug session (when spawn() is the mechanism used to start the process), the user sets the environment variable QIBM_CHILD_JOB_SNDINQMSG.
If the environment variable is assigned a numerical value, it indicates the number of descendent levels that will be enabled for debugging. This support can be used to debug applications that create children, grandchildren, great-grandchildren, and so forth. When the environment variable has a value of 1, it enables debugging of all subsequent child processes. A value of 2 enables debugging of all subsequent child processes and grandchild processes.
When the environment variable has a value less than or equal to 0, or any non-numerical value, debugging will not occur.
Here are the steps a user would take to debug an application by using spawn():
Assume the user wants to debug child processes in an application called CHILDAPP found in library MYAPPLIB.
- Set the QIBM_CHILD_JOB_SNDINQMSG environment variable to 1.
The environment variable can be set by using one of the following:
- API putenv("QIBM_CHILD_JOB_SNDINQMSG=1");
- Command ADDENVVAR ENVVAR(QIBM_CHILD_JOB_SNDINQMSG) VALUE(1)
- Command CHGENVVAR ENVVAR(QIBM_CHILD_JOB_SNDINQMSG) VALUE(1)
- Call or run the application that specifies
/QSYS.LIB/MYAPPLIB.LIB/CHILDAPP.PGM as the pathon the
spawn() invocation. CHILDAPP will start running, send a CPAA980
*INQUIRY message to the user's message queue, and then will block, waiting for
a reply to the message. Issue a Work with Active Jobs (WRKACTJOB) command and
find the CHILDAPP in a MSGW job status. Option 7 (Display message) performed
against this job will display the CPAA980 *INQUIRY message that was sent. As
part of this message, the Qualified Job Name will be displayed in the proper
format to pass to the Start Service Job (STRSRVJOB) command (for example,
145778/RANDYR/CHILDAPP).
Note: Alternatively, a Display Messages (DSPMSG) command can be issued for the user, and the output searched for the specific CPAA980 *INQUIRY message.
Note: If the job's inquiry message reply specifies using the default message reply, the child process will not block since the default reply for the CPAA980 *INQUIRY message is G.
- Issue a Start Service Job against the child process: STRSRVJOB
JOB(145778/RANDYR/CHILDAPP).
- Issue a Start Debug Command: STRDBG PGM(MYAPPLIB/CHILDAPP).
- Set whatever breakpoints are needed in CHILDAPP. When ready to continue,
find the CPAA980 message and reply with G. This will unblock CHILDAPP, which
allows it to run until a breakpoint is reached, at which time CHILDAPP will
again stop.
Note: If you reply with C to the CPAA980 message, the child process is ended before the child process' program ever receives control. In this case, on a subsequent call to wait() or waitpid(), the status information returned indicates WIFEXCEPTION(), which evaluates to a nonzero value, and WEXCEPTNUMBER() will evaluate to 0.
- The application is now stopped at a breakpoint and debugging can proceed.
If SPAWN_SETJOBNAMEPARENT_NP is set in inherit.flags, the child's i5/OS simple job name would be the same as the parent's i5/OS simple job name.
If SPAWN_SETJOBNAMEARGV_NP is set in inherit.flags, the null-terminated character string represented by argv[0] of the argv[] parameter will be used for the child's i5/OS simple job name. The name can be up to 10 characters, must be uppercase, and must contain only those characters allowed for an i5/OS job name. For example, if path was set to /QSYS.LIB/MYLIB.LIB/CHILD.PGM, SPAWN_SETJOBNAMEARGV_NP was set ON, and argv[0] was set to SON, the child's i5/OS simple job name would be SON. If the first character of the name is invalid, the path will be used. If any of the remaining characters of the name are invalid, the valid characters up to that point will be used.