What are JavaServer Pages (JSP) files?
You can use JavaServer Pages technology to create dynamic Web content while separating business logic from presentation logic. JSP files are comprised of tags (such as HTML tags and special JSP tags) and Java code. WebSphere Application Server - Express generates Java source code for the entire JSP file, compiles the code, and runs the JSP file as if it were a servlet.
HTML authors can develop JSP files that access databases and reusable Java components, such as servlets and JavaBeans. Programmers create the reusable Java components and provide the HTML authors with the component names and attributes. Database administrators or application programmers provide the HTML authors with the name of the database access and table information.
JSP lifecycle
JSP files are compiled into servlets. Thus, the JSP run-time lifecycle is similar to the servlet lifecycle. See the information below for stages of the lifecycle that are particular to JSP files.
Java source generation and compilation
When IBM HTTP Server receives a request for a JSP file, it passes the request to WebSphere Application Server - Express's servlet engine, which calls the JSP processor. The JSP processor is an internal servlet which converts a JSP file into Java source code and compiles it. The servlet that implements the JSP processor is org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspServlet.
If a certain request is the first time the JSP file has been requested or if the compiled copy of the JSP is not found, the JSP compiler generates and compiles a Java source file for the JSP file. The location of the generated files depends on which processor is being used.
The JSP syntax in a JSP file is converted to Java code that is added to the service() method of the generated class file.
Request processing
After the JSP processor has created the class file, the servlet engine creates an instance of the servlet and calls the servlet's service() method in response to the request. All subsequent requests for the JSP are handled by that instance of the servlet.
When WebSphere Application Server - Express receives a request for a JSP file, it checks to determine whether the JSP file has changed since the file was loaded. If the JSP file has changed, WebSphere Application Server - Express reloads the updated JSP (that is, the JSP processor generates an updated Java source and class file for the JSP file). The newly-loaded servlet instance receives the client request.
Accessing JSP files
JSP files can be accessed in two ways:
- The browser sends a request for a JSP file.
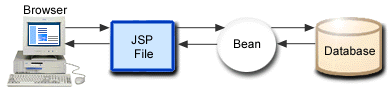
The JSP file accesses Beans or other components that generate dynamic content that is sent to the browser.
When the IBM HTTP Server receives a request for a JSP file, the server sends the request to WebSphere Application Server - Express. WebSphere Application Server - Express parses the JSP file and generates Java source, which is compiled and run as a servlet. The generation and compilation of the Java source occurs only on the first invocation of the servlet, unless the original JSP file has been updated. In such a case, WebSphere Application Server - Express detects the change, and regenerates and compiles the servlet before executing it.
- A servlet calls the JSP file.
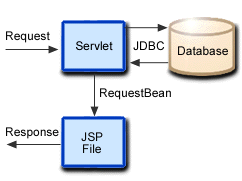
The request is sent to a servlet that generates dynamic content and calls a JSP file to send the content to the browser. This access model facilitates separating content generation from content display.

