Multiple connections to the logical unit number (LUN) from the IOA processors was implemented in V5R3, up to eight connections can be defined from multiple input/output processors on an iSeries™ server to a single LUN in the Enterprise Disk Storage. The Enterprise Disk Storage concurrently supports diverse host systems over diverse attachment protocols. Data storage is allocated among the attached host systems with the Enterprise Disk Storage Specialist, a Web-based interface. Each connection for a multipath disk unit functions independently. Several connections provide availability by allowing disk storage to be utilized even if a single path fails.
When you use multipath disk units, you must consider the implications of moving IOPs and multipath connections between nodes. You must not split multipath connections between nodes, either by moving IOPs between logical partitions or by switching expansion units between systems. If two different nodes both have connections to the same LUN in the Enterprise Disk Storage, both nodes might potentially overwrite data from the other node.
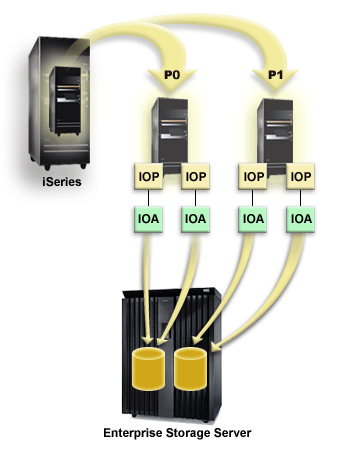
The following figure shows a logical partition configuration with multiple paths configured correctly. Partition 0 (P0) has multiple paths defined from two different IOPs to one LUN in the Enterprise Disk Storage. Partition 1 (P1) also has multiple paths defined from two different IOPs to a different LUN in the Enterprise Disk Storage. The configuration would be incorrect if each logical partition had defined connections to a single LUN.
- If you move an IOP with a multipath connection to a different logical partition, you must also move all other IOPs with connections to the same disk unit to the same logical partition.
- When you make an expansion unit switchable, make sure that all multipath connections to a disk unit will switch with the expansion unit.
- When you configure a switchable independent disk pool, make sure that all of the required IOPs for multipath disk units will switch with the independent disk pool.
Disk unit connections might be missing for a variety of reasons, but especially if one of the preceding rules has been violated. If a connection for a multipath disk unit in a system or basic disk pool is found to be missing during an IPL, a message is sent to the QSYSOPR message queue.
If a connection is missing, and you confirm that the connection has been removed, you can update Hardware Service Manager (HSM) to remove that resource. Hardware service manager is a tool for displaying and working with system hardware from both a logical and a packaging viewpoint, an aid for debugging Input/Output (I/O) processors and devices, and for fixing failing and missing hardware. You can access Hardware Service Manager in System Service Tools (SST) and Dedicated Service Tools (DST) by selecting the option to start a service tool.

Change multipath disk unit
Use the Start DASD Management Operation (QYASSDMO) API to remove the missing multiple-path disk units, resulting in only one path.
When there is a missing connection to a disk unit this message Event EV0D0401, Event Code 1E, Message ID CPI096E appears in your QSYSOPR message queue.