Virtual Ethernet creates a high speed virtual Ethernet segment that can be used to connect logical partitions in a physical iSeries™ server.
This LAN segment is separate from any real LAN that the server might have a connection with. A virtual Ethernet is made up of a virtual line description and i5/OS® TCP/IP interface. The Linux TCP/IP interface then has its own IP address but uses the virtual network device for its hardware. If a logical partition is connected only to a virtual Ethernet segment, and you want your logical partition to communicate with servers on an external LAN, you will need to bridge TCP/IP traffic between the i5/OS external LAN and the virtual i5/OS LAN segment. A logical flow of the IP packets would look something like this (Pre-V5R3 diagram):
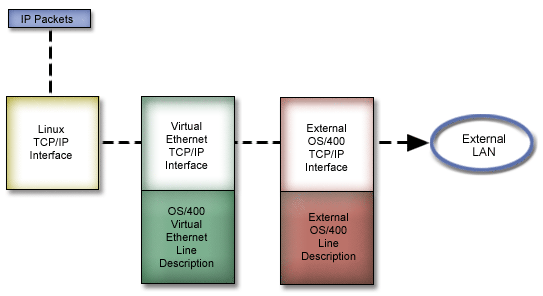
IP traffic initiated by the logical partition goes from the Linux network interface to the virtual i5/OS interface. If the virtual interface is associated with the external interface, the IP packets can continue on to the external interface and towards its destination.
There are three methods for bridging the external and virtual Ethernet segments. Each method has differences that make it useful based on your knowledge of TCP/IP and your environment. Choose from one of the following methods: