IPV4
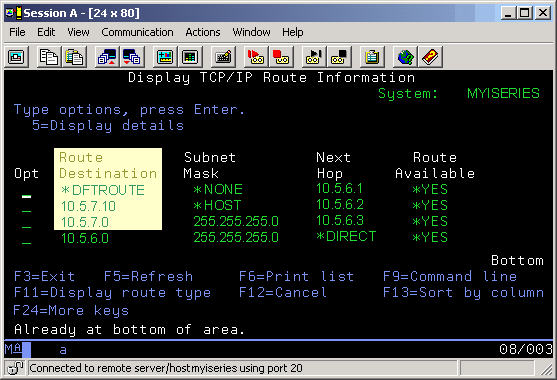
At the command line, type NETSTAT and select option 2 (Display TCP/IP route information). Verify that there is a route to the remote system specified on this display. It must be one of these types of routes: default route, host route, or network route.
This figure shows an example of each of these types of routes. Notice the values specified in the Route Destination column and the explanation of these values provided below the figure. The IP addresses 10.x.x.x represent public IP addresses. All of these addresses are for example purposes only.

| Type of Route | Route Destination value |
|---|---|
| Default Route | *DFTROUTE |
| Host Route | 10.5.7.10
This IP address should indicate the remote interface you are trying to reach. |
| Network Route | 10.5.7.0
This network address should indicate the network on which the remote interface resides. If you are not sure that the remote interface resides within the destination network, use this calculator  . . |
IPV6
At the command line, type NETSTAT and select option 5 (Display IPv6 Route Information). Verify that there is a route to the remote system specified on this display. It must be one of these types of routes: default route, host route, or network route.
This figure shows an example of each of these types of routes. Notice the values specified in the Route Destination column and the explanation of these values provided below the figure. The IP addresses 2001:DB8:x:x:x:x:x:x represent public IP addresses. All of these addresses are for example purposes only.
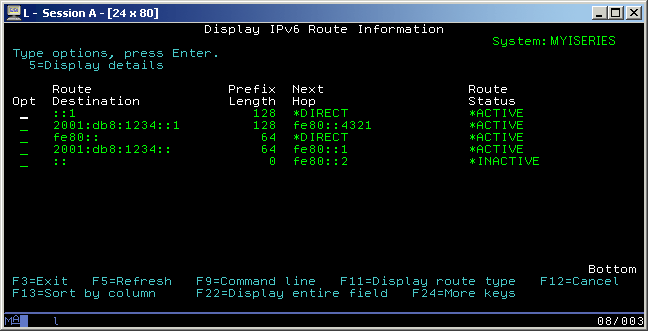
| Type of Route | Route Destination value |
|---|---|
| Default Route | ::/0 |
| Host Route | 2001:DB8:1234::1/128
This IP address should indicate the remote interface you are trying to reach. |
| Network Route | 2001:DB8:1234::/64
This network address should indicate the network on which the remote interface resides. |