You can learn how to set up two iSeries™ servers as the network DHCP server and a DHCP/BOOTP relay agent for two LANs and remote dial-in clients.
The previous example, PPP and DHCP on a single iSeries server, shows how to use PPP and DHCP on a single iSeries server to permit dial-in clients access to a network. Whether it is the physical layout of your network or security concerns, it might be more desirable to have the PPP and DHCP servers separated or to have a dedicated PPP server without DHCP services. The following figure represents a network that has dial-in clients but the PPP and DHCP policies are on different servers.
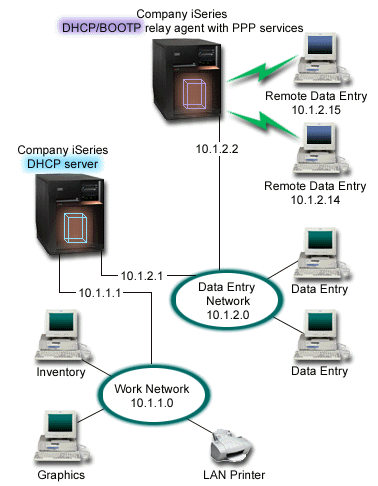
The Remote Data Entry clients dial into the iSeries PPP server. The PPP profile on that server must have a remote IP address method of DHCP like in the previous example as well as IP Forwarding in the PPP profile and the TCP/IP stack properties. Furthermore, because this server is acting as a DHCP relay agent, the BOOTP/DHCP relay agent TCP/IP server must be on. This allows the iSeries Remote Access server to pass on DHCP DISCOVER packets to the DHCP server. The DHCP server will then respond and distribute TCP/IP information to the dial-in clients through the PPP server.
The DHCP server is responsible for distributing IP addresses to both the 10.1.1.0 and 10.1.2.0 networks. In the Data Entry network, it will give out IP addresses from 10.1.2.10 to 10.1.2.40 to either dial-in or directly-attached network clients. The data entry clients also need a router address (option 3) of 10.1.2.1 to communicate with the Work network and the iSeries DHCP server must also have IP forwarding enabled.
Also, the Local Interface IP address in the PPP profile must be an IP address that falls within the subnet definition in the DHCP server. In this example, the PPP profile Local Interface address should be 10.1.2.2. This address should also be excluded from the DHCP server's address pool so that it is not assigned to a DHCP client. The Local Interface IP address must be an address to which the DHCP server can send reply packets to.
Planning the DHCP setup for DHCP with a DHCP relay agent
| Object | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration options | option 1: Subnet mask | 255.255.255.0 |
| option 6: Domain name server | 10.1.1.1 | |
| option 15: Domain name | mycompany.com | |
| Is the server performing DNS updates? | No | |
| Is the server supporting BOOTP clients? | No | |
| Object | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Subnet name | WorkNetwork | |
| Addresses to manage | 10.1.1.3 - 10.1.1.150 | |
| Lease time | 24 hours (default) | |
| Configuration options | Inherited options | Options from Global configuration |
| Subnet addresses not assigned by server | none | |
| Object | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Subnet Name | DataEntry | |
| Addresses to manage | 10.1.2.10 - 10.1.2.40 | |
| Lease time | 24 hours (default) | |
| Configuration options | option 3: Router | 10.1.2.1 |
| Inherited options | Options from Global configuration | |
| Subnet addresses not assigned by server | 10.1.2.1 (Router) |
|
Other setup on the iSeries server running PPP
- Set up the BOOTP/DHCP relay agent TCP/IP server
Object Value Interface address 10.1.2.2 Relay packets to Server IP address 10.1.2.1 - Set the Remote IP address method to DHCP in the PPP receiver connection
profile
- Enable DHCP WAN client connection with a DHCP server or relay connection using the Services menu item for Remote Access Services in iSeries Navigator
- Select to Use DHCP for the IP address assignment method under the TCP/IP Settings Properties of the Receiver Connection Profile in iSeries Navigator
- Allow remote system to access other networks (IP forwarding) under the TCP/IP Settings Properties of the Receiver Connection Profile in iSeries Navigator (to allow the remote clients to communicate with the Data Entry Network)
- Enable IP datagram forwarding under the Settings Properties of the TCP/IP Configuration in iSeries Navigator (to allow the remote clients to communicate with the Data Entry Network)