The IBM®  iSeries™ system provides support for direct
and bridged frame-relay network connections.
iSeries™ system provides support for direct
and bridged frame-relay network connections.
- Direct frame-relay network
- The direct frame-relay network allows communications using Systems Network Architecture (SNA) or TCP/IP data over a frame-relay network at speeds of up to 2.048 Mbps. This support allows a network of systems to communicate using the frame-relay network as a backbone without the need for multiple-leased T1 lines. This function is also known as boundary network node (BNN) support.
- Bridged frame-relay network
- The bridged frame-relay network allows the iSeries system
to communicate over a frame-relay network. This communication takes place
through a remote bridge that is attached to a token-ring, Ethernet, or distributed
data interface (DDI) network. Bridged frame-relay connections allow the iSeries system
to communicate with stations on the remote local area network (LAN) as if
they were attached locally to the LAN. This function is also known as boundary
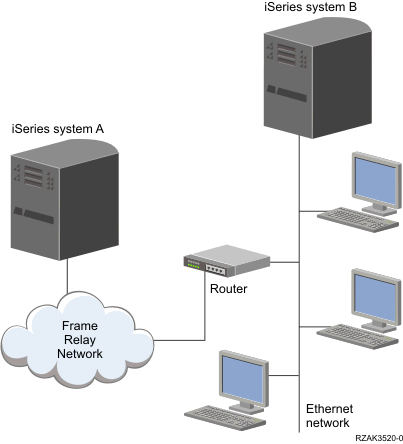
access node (BAN) support. Figure 1 shows
an example of a bridged frame-relay connection.
In this example, iSeries System A communicates through the frame-relay network and the bridge to iSeries System B. Bridged frame-relay connections support SNA and TCP/IP data communications.