Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol that extends PPP to support a link layer tunnel between a requesting L2TP client (L2TP Access Concentrator or LAC) and a target L2TP server endpoint (L2TP Network Server or LNS).
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol
By using Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) tunnels, it is possible to separate the location at which the dial-up protocol ends and where the access to the network is provided. That is why L2TP is also referred to as Virtual PPP.
An Internet Service Provider (ISP) uses the virtual line mode to operate virtual private networks (VPN). See Configure an L2TP connection protected by VPN for a better understanding of how IPSec works with L2TP.
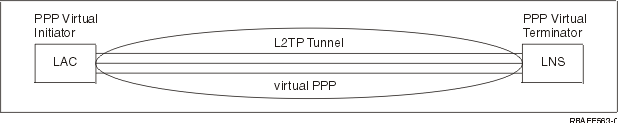
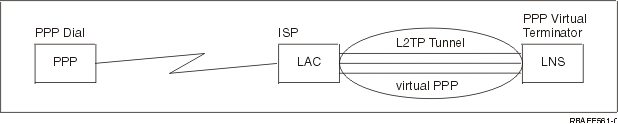
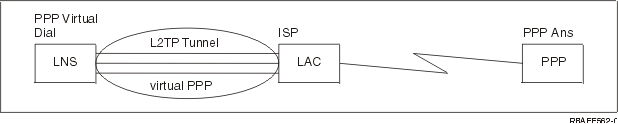
The L2TP protocol is documented as a Request For Comment standard, RFC2661. More information about RFCs can be found on the RFC Editor Web page. An L2TP tunnel can extend across an entire PPP session or only across one segment of a two-segment session. This can be represented by four different tunneling models: