A cluster using switched disk technology provides an alternative to having the data replicated. In a switched disk cluster, the data is actually contained in independent disk pools (also referred to as independent ASPs).
This example configuration provides the following:
- One switchable independent disk pool with an idle standby server. The independent disk pool is contained within a collection of disk units that are switchable.
- Two-tier environment
- Applications and data move together
- Backup used for different work loads not associated with this application's data
- No data replication; only one copy of the data exists in this cluster
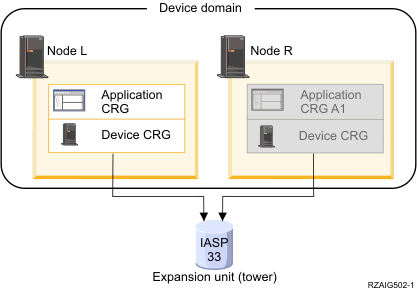
Using this example, Node L and Node R belong to the same device domain. Node L is currently operating as the primary node for two cluster resource groups - an application CRG and a device CRG. Node R is the first (and only) backup for both of the cluster resource groups. Data that is associated with the device CRG is contained in a switchable resource such as an external expansion unit (tower). Pertinent application information associated with the application CRG is either stored in that same tower or is otherwise being replicated from Node L to Node R. If Node L fails or needs to be taken down for administrative reasons, then Node R becomes the primary node for both cluster resource groups. Node R will take over the Internet Protocol (IP) address defined for the application CRG. Node R will also assume ownership of the switchable resource defined for the device CRG.