This proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) method uses transparent subnetting to associate a partition's virtual interface with an external interface. Proxy ARP function is built into the TCP/IP stack. If you have the necessary IP addresses, this approach is recommended.
- V4 TCP/IP for AS/400®: More Cool Things Than Ever

This IBM® Redbook provides sample scenarios that demonstrate common solutions with example configurations. It also helps you plan, install, tailor, configure, and troubleshoot TCP/IP on your iSeries™ server.
- TCP/IP
routing and workload balancing
This topic provides techniques and instructions for routing and workload balancing.
If you choose to use the proxy ARP method, you must have a firm understanding of subnetting and TCP/IP. You need to obtain a contiguous block of IP addresses that are routable by your network. You subnet this block of IP addresses. In this example, a contiguous block of four IP addresses (10.1.1.72 through 10.1.1.75) is used. Because it is a block of four IP addresses, the subnet mask for these addresses is 255.255.255.252. You assign one to each of the virtual TCP/IP interfaces on your partitions as shown in this figure.
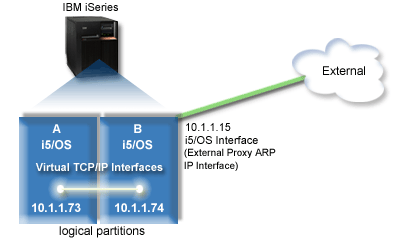
In this example, TCP/IP traffic from partition A runs across the virtual Ethernet to the 10.1.1.74 interface on partition B. Because10.1.1.74 is associated with the external proxy ARP interface 10.1.1.15, the packets continue out of the virtual Ethernet using the proxy ARP interface.
To configure a virtual Ethernet to use the proxy ARP connection method, complete these configuration tasks.