In addition to creating secure applications using the GSKit APIs, you can also use the SSL_ APIs. SSL_ APIs only exist in the i5/OS™ operating system.
The following figure shows the socket and SSL_APIs used to create a secure server.
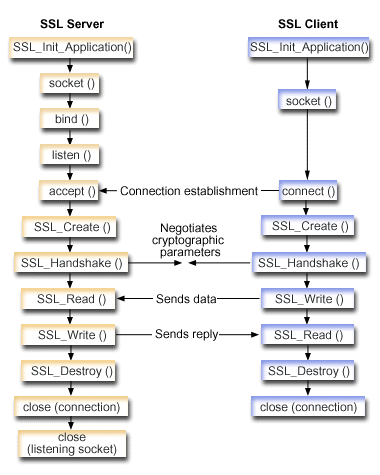
Socket flow of events: Secure server that uses SSL_ APIs
The following description shows the relationship between the APIs that enable an SSL server to perform and communicate with an SSL client:
- Either call SSL_Init() or SSL_Init_Application() to
initialize the job environment for SSL processing and to establish the SSL
security information for all SSL sessions that run in the current job. Only
one of these APIs should be used. It is preferred that you use the SSL_Init_Application() API.
Note: The following example program uses the SSL_Init_Application API.
- The server calls socket() to obtain a socket descriptor.
- The server calls bind(), listen(), and accept() to activate a connection for a server program.
- The server calls SSL_Create() to enable SSL support for the connected socket.
- The server calls SSL_Handshake() to initiate the SSL handshake negotiation of the cryptographic parameters.
- The server calls SSL_Write() and SSL_Read() to send and receive data.
- The server calls SSL_Destroy() to disable SSL support for the socket.
- The server calls close() to destroy the connected sockets.
Socket flow of events: Secure client that uses SSL_ APIs
- Either call SSL_Init() or SSL_Init_Application() to
initialize the job environment for SSL processing and to establish the SSL
security information for all SSL sessions that run in the current job. Only
one of these APIs should be used. It is preferred that you use the SSL_Init_Application API.
Note: The following example program uses the SSL_Init_Application API.
- The client calls socket() to obtain a socket descriptor.
- The client calls connect() to activate a connection for a client program.
- The client calls SSL_Create() to enable SSL support for the connected socket.
- The client calls SSL_Handshake() to initiate the SSL handshake negotiation of the cryptographic parameters.
- The client calls SSL_Read() and SSL_Write() to receive and send data.
- The client calls SSL_Destroy() to disable SSL support for the socket.
- The client calls close() to destroy the connected sockets.
Note: The sample uses AF_INET address family; however, it can
be modified to use the AF_INET6 address family. By using the code examples,
you agree to the terms of the Code license and disclaimer information.
/* SSL Server Program using SSL_Init_Application */
/* Assummes that application id is already registered */
/* and a certificate has been associated with the */
/* application id. */
/* No parameters, some comments and many hardcoded */
/* values to keep it short and simple */
/* use following command to create bound program: */
/* CRTBNDC PGM(MYLIB/SSLSERVAPP) */
/* SRCFILE(MYLIB/CSRC) */
/* SRCMBR(SSLSERVAPP) */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <qsossl.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <errno.h>
void main(void)
{
SSLHandle *sslh;
SSLInitApp sslinit;
struct sockaddr_in address;
int buf_len, on = 1, rc = 0, sd, lsd, al;
char buff[1024];
/* only want to use 1 cipher suite */
unsigned short int cipher = SSL_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA;
void * malloc_ptr = (void *) NULL;
unsigned int malloc_size = 8192;
/* memset sslinitapp structure to hex zeros */
memset((char *)&sslinit, 0, sizeof(sslinit));
/* fill in values for sslinit app structure */
sslinit.applicationID = "MY_SERVER_APP";
sslinit.applicationIDLen = 13;
sslinit.localCertificate = NULL;
sslinit.localCertificateLen = 0;
sslinit.cipherSuiteList = NULL;
sslinit.cipherSuiteListLen = 0;
/* allocate and set pointers for certificate buffer */
malloc_ptr = (void*) malloc(malloc_size);
sslinit.localCertificate = (unsigned char*) malloc_ptr;
sslinit.localCertificateLen = malloc_size;
/* initialize ssl call SSL_Init_Application */
rc = SSL_Init_Application(&sslinit);
if (rc != 0)
{
printf("SSL_Init_Application() failed with rc = %d and errno = %d.\n",
rc,errno);
return;
}
/* initialize a socket to be used for listening */
lsd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (lsd < 0)
{
perror("socket() failed");
return;
}
/* set socket so can be reused immediately */
rc = setsockopt(lsd, SOL_SOCKET,
SO_REUSEADDR,
(char *)&on,
sizeof(on));
if (rc < 0)
{
perror("setsockopt() failed");
return;
}
/* bind to the local server address */
memset((char *) &address, 0, sizeof(address));
address.sin_family = AF_INET;
address.sin_port = 13333;
address.sin_addr.s_addr = 0;
rc = bind(lsd, (struct sockaddr *) &address, sizeof(address));
if (rc < 0)
{
perror("bind() failed");
close(lsd);
return;
}
/* enable the socket for incoming client connections */
listen(lsd, 5);
if (rc < 0)
{
perror("listen() failed");
close(lsd);
return;
}
/* accept an incoming client connection */
al = sizeof(address);
sd = accept(lsd, (struct sockaddr *) &address, &al);
if (sd < 0)
{
perror("accept() failed");
close(lsd);
return;
}
/* enable SSL support for the socket */
sslh = SSL_Create(sd, SSL_ENCRYPT);
if (sslh == NULL)
{
printf("SSL_Create() failed with errno = %d.\n", errno);
close(lsd);
close(sd);
return;
}
/* set up parameters for handshake */
sslh -> protocol = 0;
sslh -> timeout = 0;
sslh -> cipherSuiteList = &cipher;
sslh -> cipherSuiteListLen = 1;
/* initiate the SSL handshake */
rc = SSL_Handshake(sslh, SSL_HANDSHAKE_AS_SERVER);
if (rc != 0)
{
printf("SSL_Handshake() failed with rc = %d and errno = %d.\n",
rc, errno);
SSL_Destroy(sslh);
close(lsd);
close(sd);
return;
}
/* memset buffer to hex zeros */
memset((char *) buff, 0, sizeof(buff));
/* receive a message from the client using the secure session */
rc = SSL_Read(sslh, buff, sizeof(buff));
if (rc < 0)
{
printf("SSL_Read() rc = %d and errno = %d.\n",rc,errno);
rc = SSL_Destroy(sslh);
if (rc != 0)
printf("SSL_Destroy() rc = %d and errno = %d.\n",rc,errno);
close(lsd);
close(sd);
return;
}
/* write results to screen */
printf("SSL_Read() read ...\n");
printf("%s\n",buff);
/* send the message to the client using the secure session */
buf_len = strlen(buff);
rc = SSL_Write(sslh, buff, buf_len);
if (rc != buf_len)
{
if (rc < 0)
{
printf("SSL_Write() failed with rc = %d.\n",rc);
SSL_Destroy(sslh);
close(lsd);
close(sd);
return;
}
else
{
printf("SSL_Write() did not write all data.\n");
SSL_Destroy(sslh);
close(lsd);
close(sd);
return;
}
}
/* write results to screen */
printf("SSL_Write() wrote ...\n");
printf("%s\n",buff);
/* disable SSL support for the socket */
SSL_Destroy(sslh);
/* close the connection */
close(sd);
/* close the listening socket */
close(lsd);
return;
}