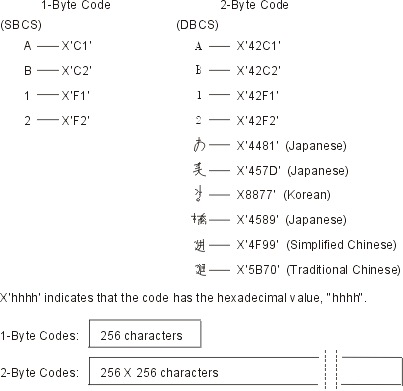
Some languages, such as Chinese, Japanese, and Korean, have a writing scheme that uses many different characters that cannot be represented with single-byte codes. To create coded character sets for such languages, the server uses two bytes to represent each character. Characters that are encoded in two-byte code are called double-byte characters.
Figure 1 shows alphanumeric characters coded in a single-byte code scheme and double-byte characters coded in a double-byte code scheme.
You can use double-byte characters as well as single-byte characters in one application. For instance, you might want to store double-byte data and single-byte data in your database, create your display screens with double-byte text and fields, or print reports with double-byte characters.