A window is created using a window and a low-level environment description. The window description provides the window attributes, a pointer to data that is specified by the using application, and several exit routines that the window module calls when a window is moved, resized, or deleted so the using program can perform the appropriate actions. The low-level environment description is the same as that used on the Create Low-Level Environment (QsnCrtEnv) API to create a low-level environment. A window is implemented as a low-level environment where the user data pointer describes the window itself. Thus, a window can be manipulated through the low-level APIs or through the window APIs by using the same window handle. This implementation is similar to the concept of inheritance in object-oriented programming languages. DSM window support uses graphical user interface (GUI) when the underlying control unit supports it.
Each window has the low-level environment window mode enabled. The low-level environment window area is set to the usable area in the window, which consists of the area inside the border and attributes that can be accessed by screen I/O services. (It does not include the message line.) Use relative coordinates when specifying a row and column on an I/O API. The upper left corner of the usable area is (1,1). To use absolute coordinates with a window, disable the low-level environment window mode with the Set Low-Level Environment Window Mode (QsnSetEnvWinMod) API.
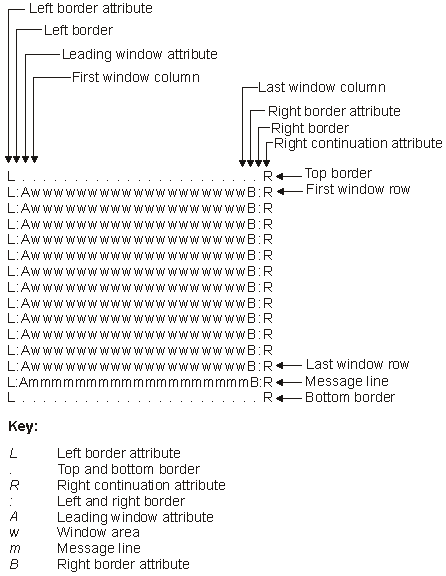
Figure 1 shows the components of a DSM window. The window in this example has a specified depth of 13 rows and a width of 19 columns.
The attributes of a DSM window are similar to those of a data description specifications (DDS) window. The initial size and location of a DSM window are specified using the location of the upper-left window border character and the number of rows and columns within the window. For DSM windows, the leading window attribute, right continuation attribute, or message line can be specified separately. Unlike a DDS window, a DSM window does not require the following:
If a window is defined with no border, no extra space is used on the display for the border characters or their attributes (L and B in Figure 1). An area of the screen is cleared starting from the specified location for the upper left corner of the window and continues for the number of rows and columns given as the window size. Figure 2 shows an example of a window with no border.
Note: In discussions throughout the DSM sections that refer to window borders, this should be taken to mean the top/bottom window row or left/right window column for a window with no borders.
If a window is defined with no border attributes (L and B in Figure 1), no extra space for these is used on the display. Figure 3 shows a window with no border attributes.
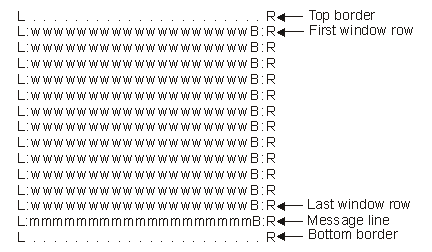
The leading window attribute (A in Figure 1) is part of the addressable window area. If specified, this attribute takes up an extra screen character and does not reduce the size of the window area. Figure 4 shows a window defined with no leading window attribute. The window text directly follows the window border character. Attribute characters can be written inside the window if desired.
If the right continuation attribute (R in Figure 1) is specified on a window description, DSM determines the appropriate attribute to use, based on the screen image underlying the window. If the window is not a GUI window, right-continuation-attribute correction is performed for display-screen and presentation screen DBCS-only attributes. (No correction is performed for extended primary attributes and DBCS data types). When a window is placed on a screen that supports extended attributes, all extended attributes are cleared prior to displaying the window. To have the right continuation attribute handle extended attributes, you must use a display that supports GUI windows and specify GUI window support on the window description.
Specifying a message line on a window description decreases the number of lines in the window area by 1, as shown in Figure 1.

| Key | |
|---|---|
| L | Left border attribute |
| . | Top and bottom border |
| R | Right continuation attribute |
| : | Left and right border |
| A | Leading window attribute |
| w | Window area |
| m | Message line |
| B | Right border attribute |
Figure 2. DSM Window with No Border
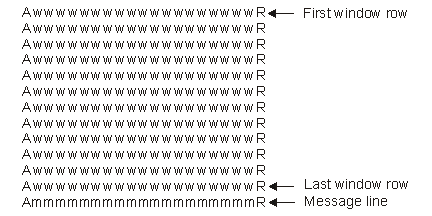
Figure 3. DSM Window with No Border Attributes
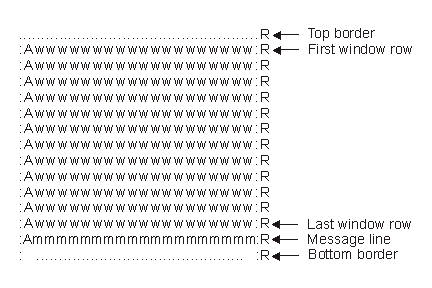
Figure 4. DSM Window with No Leading Window Attribute
| Top | Dynamic Screen Manager APIs | APIs by category |