A path name (also called a pathname on some systems) tells the server how to locate an object.
The path name is expressed as a sequence of directory names followed by the name of the object. Individual directories and the object name are separated by a slash (/) character; for example:
directory1/directory2/file
For your convenience, the backslash (\) can be used instead of the slash in integrated file system commands.
There are two ways of indicating a path name:
- An absolute path name begins at the
highest level, or "root" directory (which is identified by the / character).
For example, consider the following path from the / directory to the file
named Smith. Figure 1. The components of a path name
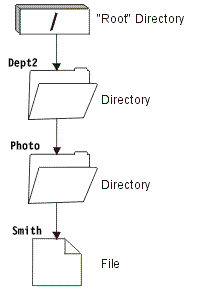
The absolute path name to the Smith file is as follows:
/Dept2/Photo/Smith
The absolute path name is also known as the full path name.
- If the path name does not begin with the / character, the system assumes
that the path begins at your current directory. This type of path name is
called a relative path name. For example,
if your current directory is Dept2 and it has a subdirectory named Photo
containing the file Smith, the relative path name to the file is:
Photo/Smith
Notice that the path name does not include the name of the current directory. The first item in the name is the directory or object at the next level below the current directory.